We welcome you to the official site of the Research Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Bishkek city.
Federal State Budget Institution of Science Research Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Bishkek city is the research organization subordinated to the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russia Federation.
The Research Station of RAS engages 57 scientific workers, including 26 researchers, 2 Doctors of Sciences and 8 Candidates of Sciences among them. The overall staff amounts 133 employees.
Address
![]()
720049, Kyrgyzstan.
Bishkek-49, Research Station RAS.
Phone: +996 (312) 613-140
Fax: +996 (312) 611-459
Director
XVI International Conference of Young Scientists and Students "MODERN EQUIPMENT AND TECHNOLOGIES IN SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH"
Dear colleagues!
On April 24-26, 2024, the XVI International Conference of Young Scientists and Students "MODERN EQUIPMENT AND TECHNOLOGIES IN SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH" was held at the Research Station of Russian Academy of Sciences in Bishkek (Kyrgyz Republic).

The collection of Conference materials is registered with the Book Chamber of the Kyrgyz Republic (ISBN 978-9967-12-986-3). The electronic version of the collection is available at link: https://cloud.mail.ru/public/GiyK/q29otLb7R , as well as on the Conference website in the "Archive" section http://mmk.gdirc.kg/archive/
Currently, the collection of materials is undergoing the stage of placement in the information and analytical system of the RSCI (https://elibrary.ru/). We will inform you about the results by an additional letter.
Olga Zabinyakova
Academic Secretary of RS RAS
This e-mail address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it
+996 (312) 61-31-40
Last Updated on Friday, 22 November 2024 14:46
Visit of RAS academicians to Research Station of RAS
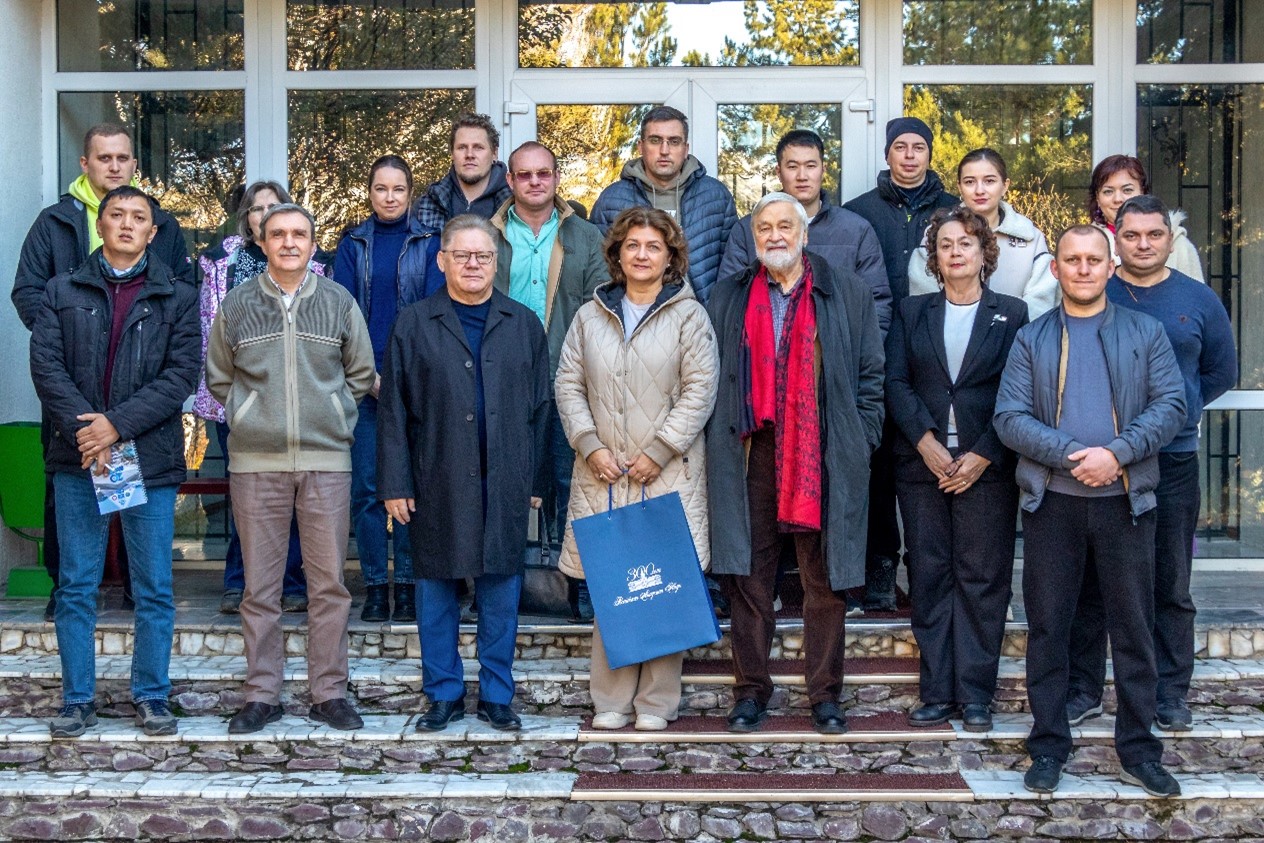

On October 31, 2024, the RAS leadership delegation visited the Research Station with a working visit. The delegation included Deputy President of the RAS - Academician of RAS Petr Aleksandrovich Chekmarev, Deputy Chairman of the National Committee of Geologists of Russia - Academician of RAS Alexander Olegovich Gliko and Chief Specialist of the Department of International Regional Programs and Projects of RAS - Inna Leonidovna Syrus. The heads of the Research Station laboratories acquainted the guests with the scientific directions of the laboratories and the results of their activities. During the excursion, the delegation got acquainted with the infrastructure, activiry, working conditions and features of conducting field experimental work in the mountainous conditions of the Tien Shan.

Last Updated on Tuesday, 05 November 2024 14:12
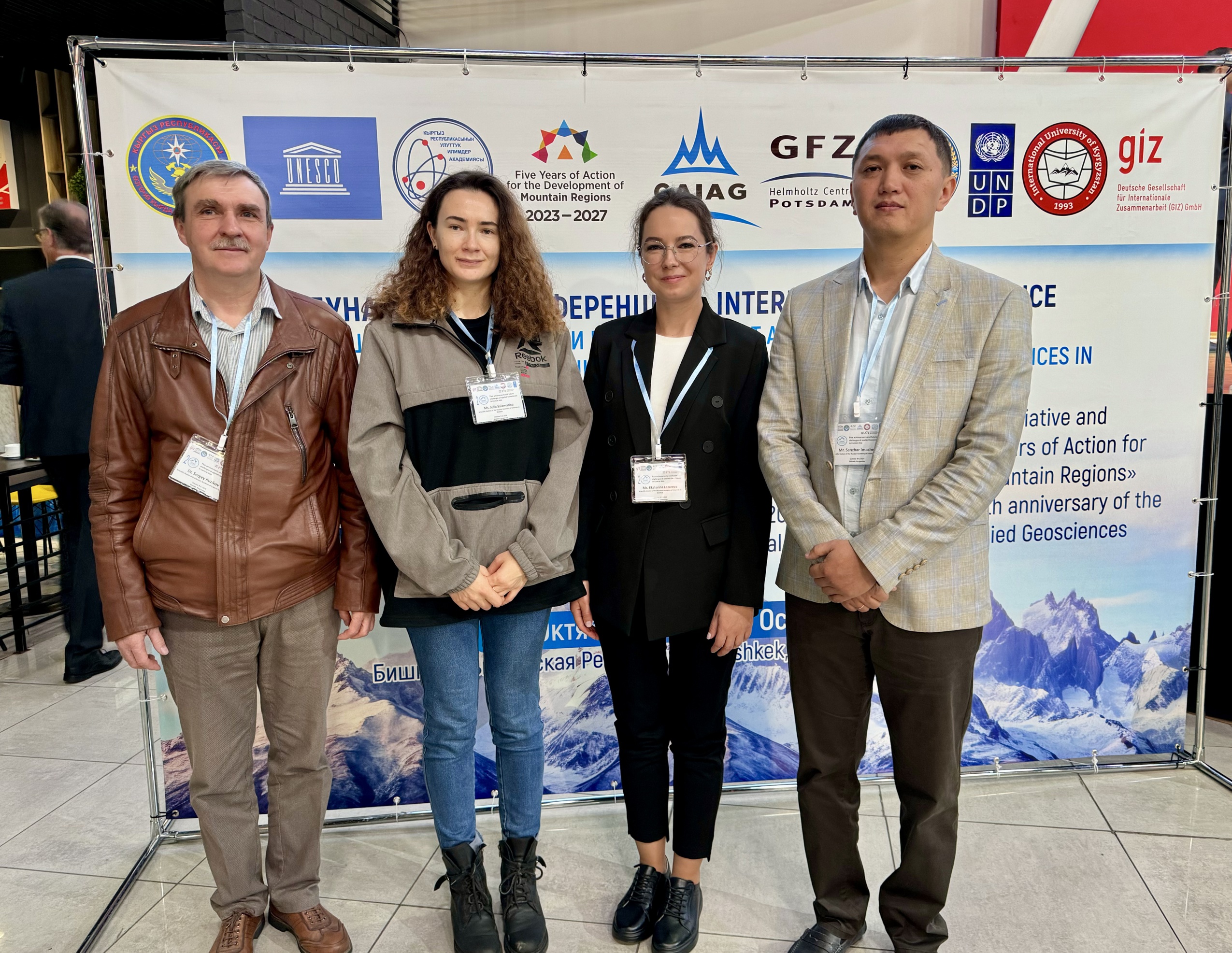
20th Anniversary of the CAIAG
On October 8-9, 2024, the Anniversary Conference with international participation dedicated to the 20th anniversary of the Central Asian Institute of Applied Geosciences (CAIAG) on the topic "Past achievements and future challenges of applied geosciences in Central Asia" was held. The conference was held at the International University of Kyrgyzstan (Bishkek).
The staff of the RAS took an active part throughout the entire duration of the conference in the section "Dangerous Natural Processes and Phenomena in Central Asia".

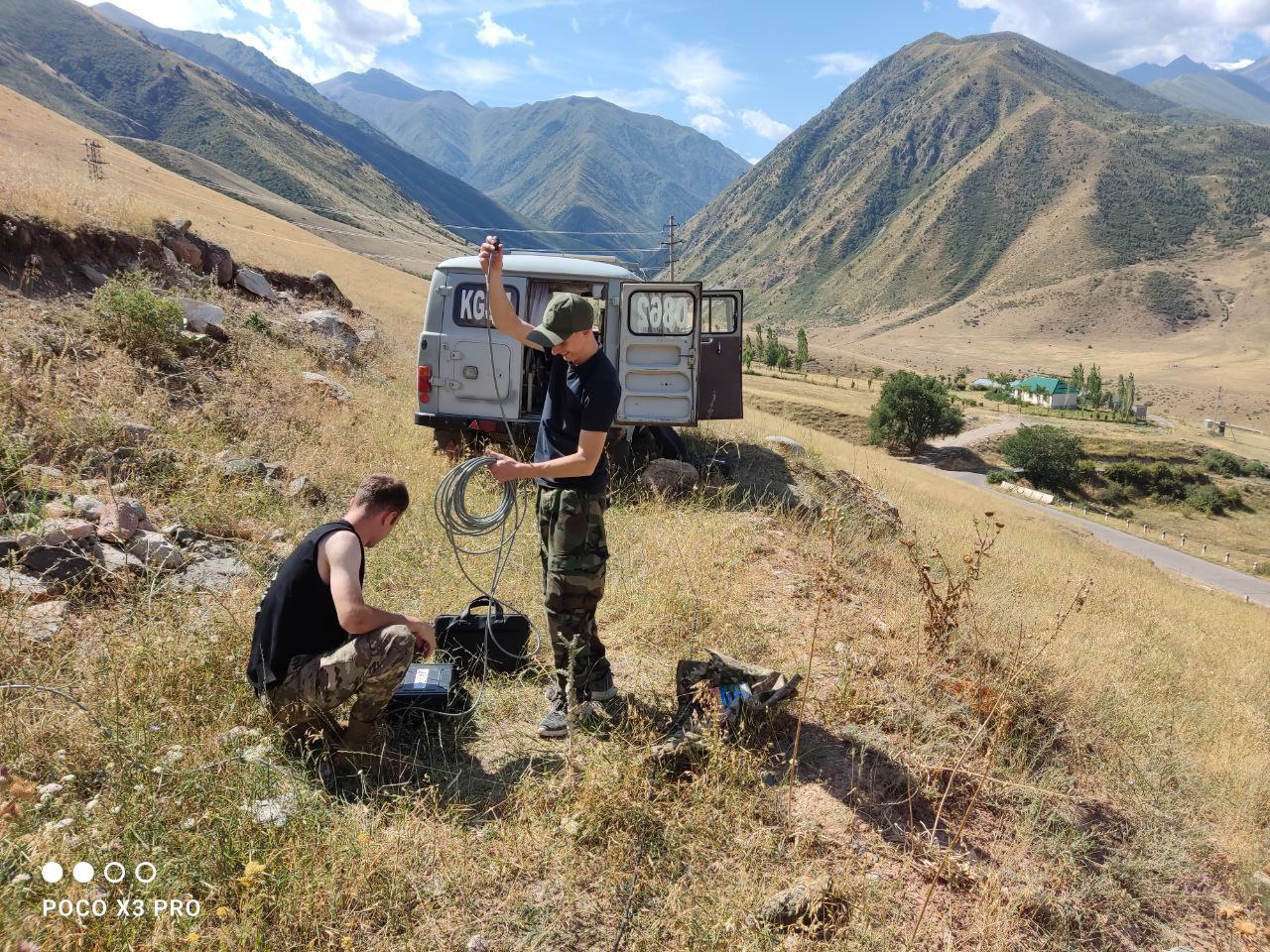
Group of electromagnetic observations (GEO) news (Laboratory of Integrated Studies)
In August 2024, the staff of the Group of electromagnetic observations (GEO) of the Laboratory of Integrated Studies (LIS) resumed experimental work on the study of seismic and acoustic response of the geo-environment to sensing by electric pulses of the ERGU-600 electric exploration generator set. On August 12, 2024, measurements were made at the Southern Dipole field observation point by a mobile receiving station organized on the UAZ basis.

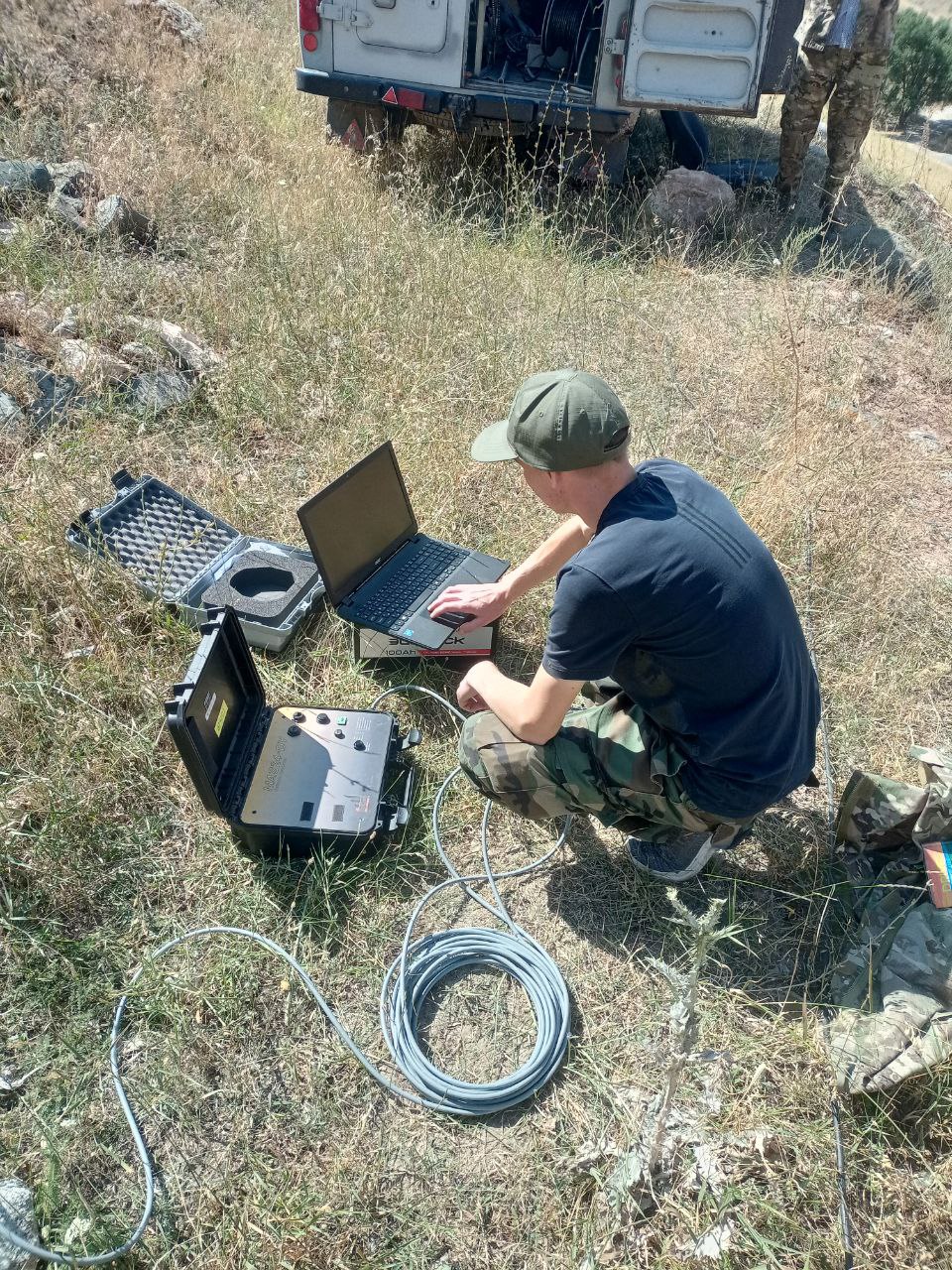
The registration of geoacoustic signal was carried out using the DYMAS-24 mobile digital system with a Veloget-3D triaxial geophone at the outcrops of bedrock near the feeding dipole. To view and analyze the measurements, a special data preprocessing program of the DYMAS-24 "EveProc" geoacoustic signal registration system was used, developed by LIS employees. Together with this, geomagnetic observations were carried out with the registration of the full vector of the magnetic field T, for which the MV-07 magnetic variation modular station was used.
The observations carried out by the laboratory make it possible to obtain additional qualitative information that can be used in the analysis of spatial and temporal features of deformation processes occurring within the polygon and its surroundings, as well as in the interpretation of data using other geophysical methods.

Last Updated on Tuesday, 01 October 2024 08:22
Regional GNSS measurements on the territory of Kyrgyzstan in 2024. KGS24a, KGS24b.
This year, the field group of the GPS Laboratory (LGPS) based on the Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) method conducts planned field measurements of GNSS network points on the territory of the Chui, Jalal-Abad, Talas, Issyk-Kul, Naryn regions of Kyrgyzstan within the framework of the State Assignment: "Study of modern movements of the earth's crust of the Tien Shan and adjacent territories by methods of ground and space geodesy" reg. No. 1021052806451-5-1.5.1.
Repeated surveys of the same GNSS points in the study area make it possible to determine the high-precision position of the point at the time of measurement and track the long-term rate of its displacement to solve fundamental geodynamic problems, as well as to assess the danger to the population and vital facilities. From May to September 2024, LGPS employees traditionally carry out two campaigns (KGS24a from 04.07.2024 to 03.08.2024; KGS24b from 21.08.2024 to 16.09.2024).
Each team includes an operator and a driver of a ZIL-131 or GAZ-33088 vehicle. Each team measures 14-15 points per month, with 36 hours allocated for each point. The vehicle mileage during one campaign was 1,500-2,200 km. The average vehicle mileage between observation points was 130 km. Since 2020, GSDN employees have been taking GNSS measurements using Russian-made MP-8 receivers capable of recording signals from 4 satellite constellations: GPS, GLONASS, Beidou and SBAS (Fig. 2).
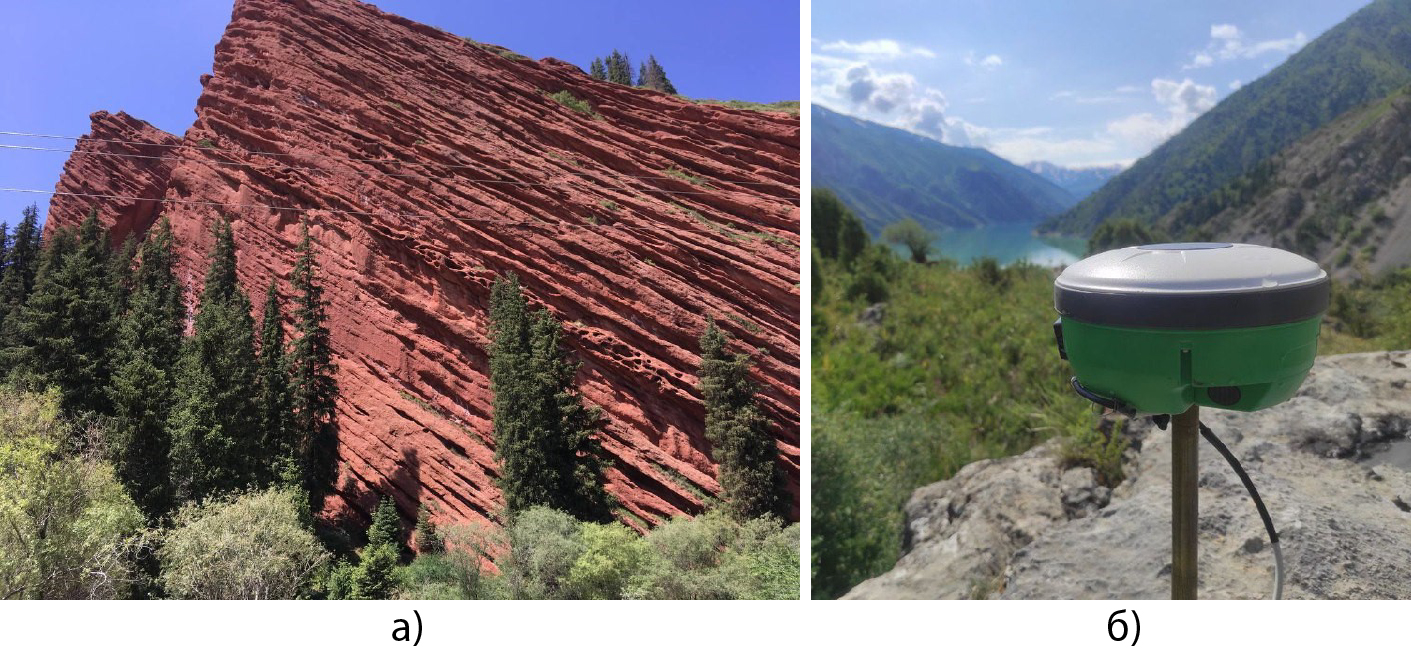

Figure 1 – Fragments of field GNSS work in 2024:
a) Field landscape of the team from the measurement site of the regional GNSS point;
b) Measurement at the GNSS point with the MP-8 receiver with a pin support.
Last Updated on Thursday, 19 September 2024 11:15
News of the Laboratory of Advanced Hardware Development (LAHD)
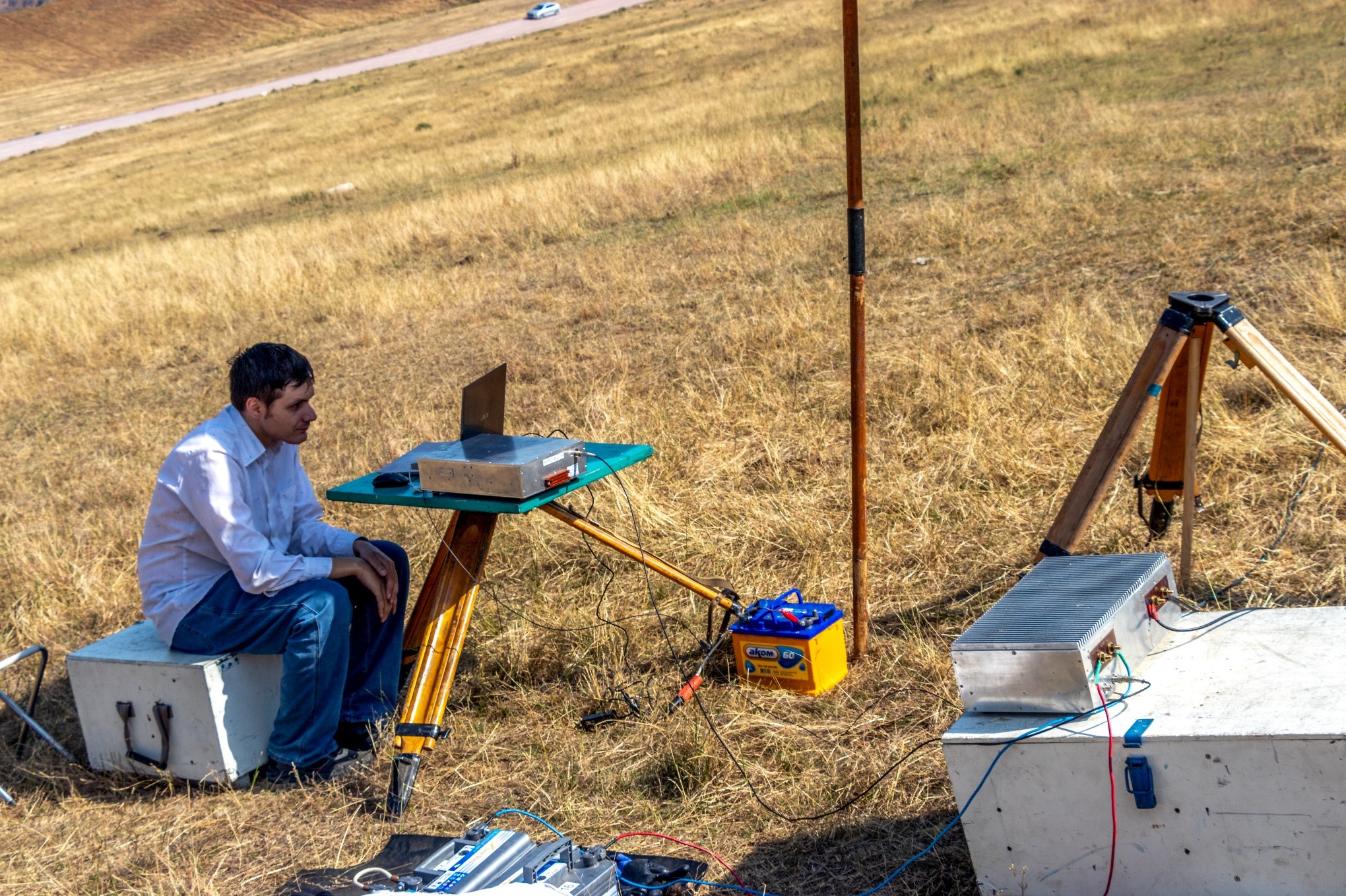
On August 15, 2024, a series of experiments were conducted in the Chunkurchak gorge to test the technology of electromagnetic monitoring of the earth's crust stress-strain state using experimental electrical exploration measuring complex with pseudonoise signals developed at the Laboratory of Advanced Hardware Development (LAHD).
The main objective of the experiments is to test the sounding frame with a long side equal to 100 m introduced into the equipment. Previously, experiments were conducted with a frame with a long side equal to 50 m. Experiments were conducted with both a 50x50 frame and a 100x100 meter frame. The data obtained will allow a comparative assessment of the effectiveness (increase in depth) of probing with an increase in the area of sounding frame.

News of the Group of New Technologies Introduction (GNTI)
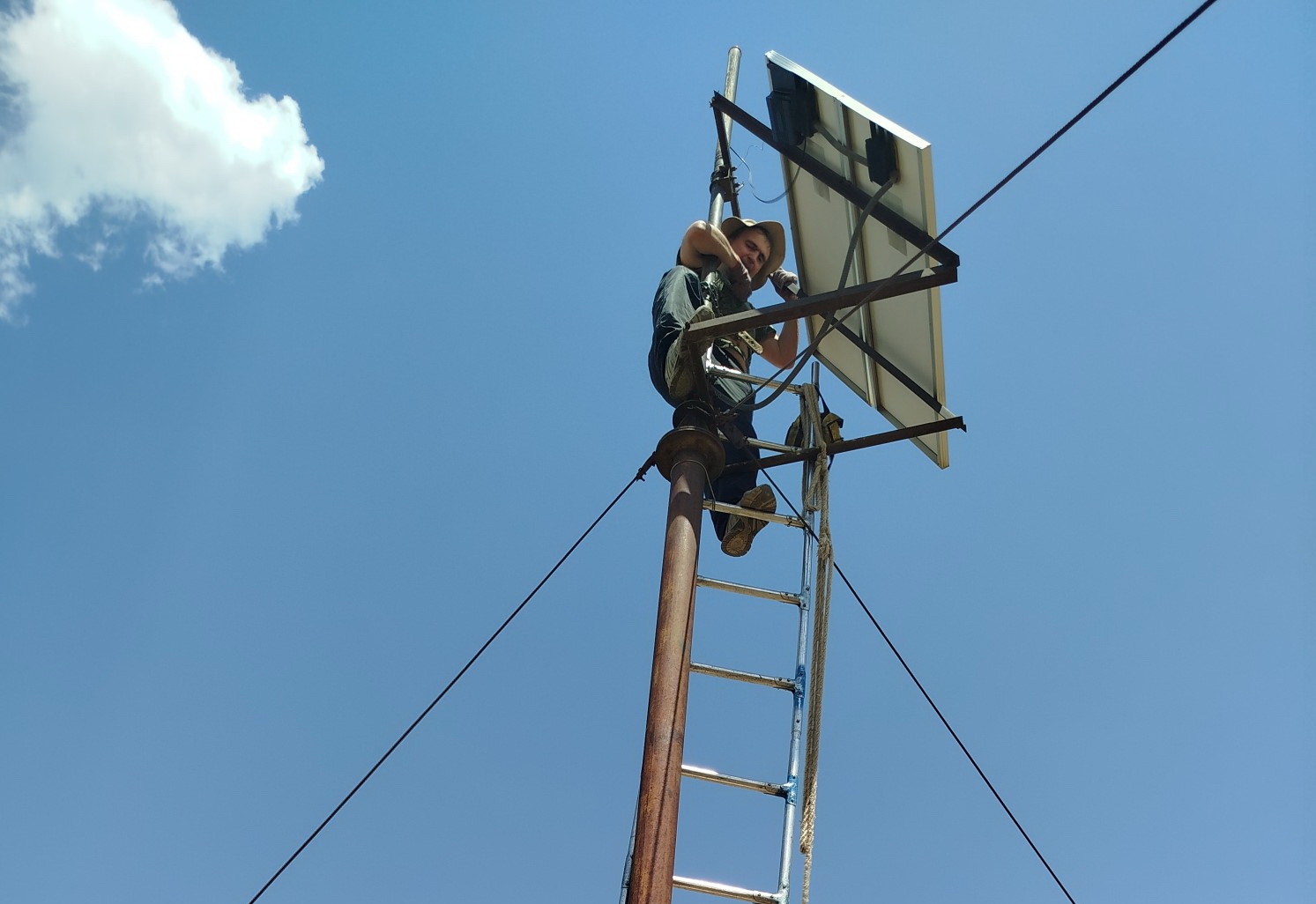
On May 16-18, 2024, the GNTI employees upgraded the equipment of KAZA permanent GPS station, located near the Kazarman village. The LTE router was installed, which allows receiving data on a daily basis, as well as promptly monitoring the station operation. Earlier, data was delivered 8 times a year through a personal visit to the station, which led to high operating costs.
The KAZA station was launched in July 1997 in a joint project with NASA and is distinguished by high quality and stability of data.

GMTS News
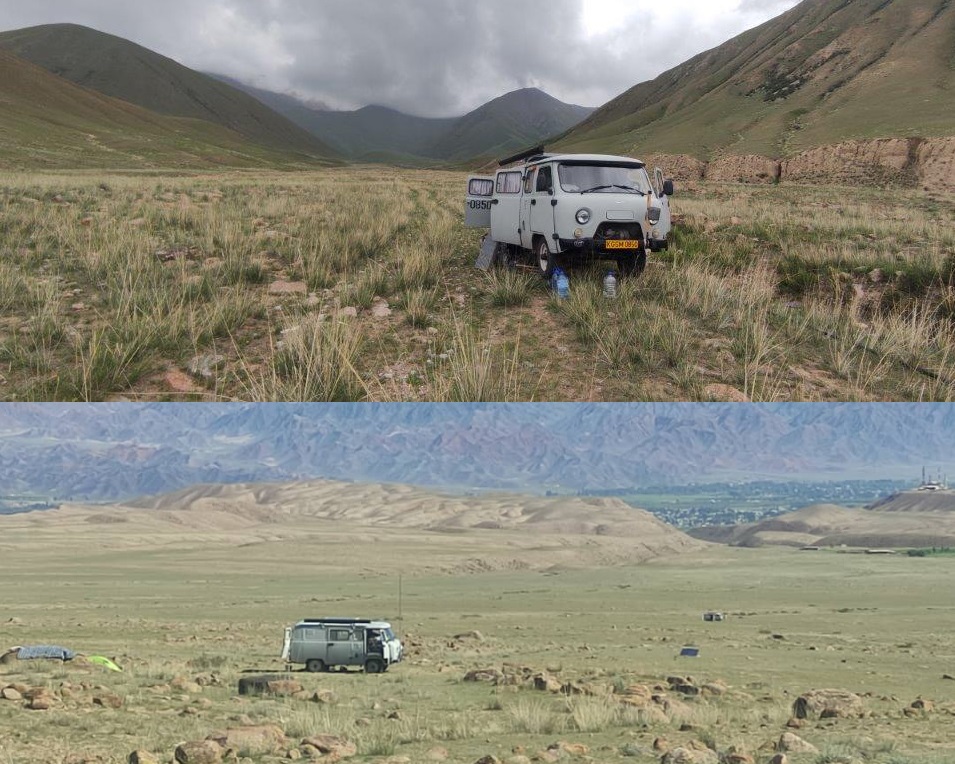
In the period from July 16 to August 6, the MTS group consisting of 2 teams carried out work on the Ukok-2 profile, which is located south of the Kochkorka in the Kochkor district of the Naryn region. The works was carried out on magnetotelluric sounding (MTS) at 11 points. At 10 observation points, the duration of MT-field registration in the MTS mode was 36-43 hours, at the FT21 observation point in the DMTS mode, the registration was performed in the form of two registration sessions, the duration of each was about 240 hours.
The works was carried out using Phoenix MTU-5 measuring complexes in the standard recording mode. The start of the work was preceded by calibrations of the recorders and sensors of the MT stations. At all observation points, a control recording lasting at least 40 minutes was made to assess the level of interference and adjust the recording parameters of the working record.
The MT field electric components were measured using measuring installations with 50 m long electric dipoles. The magnetic field components were measured using MTS-50 induction sensors. At all sounding points, dipole grounding was performed using non-polarizing electrodes; dipole grounding was performed according to the “sensor to sensor” principle from previous years of observations. The orientations of the measuring installations at these points completely repeated the previous deployments.

Last Updated on Tuesday, 03 September 2024 10:43
More Articles...
- Excursion to Issyk-Ata gorge and regime station "Issyk-Ata"
- Solution of the IX International Symposium
- XVI International Conference of Young Scientists and Students «Modern Equipment and Technologies in Scientific Research» - 2024
- IX International Symposium
- Results of publication activity of staff of the Research Station of the Russian Academy of Sciences for 2023
Page 1 of 25
Last news
- XVI International Conference of Young Scientists and Students "MODERN EQUIPMENT AND TECHNOLOGIES IN SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH"
- Visit of RAS academicians to Research Station of RAS
- 20th Anniversary of the CAIAG
- Group of electromagnetic observations (GEO) news (Laboratory of Integrated Studies)
- Regional GNSS measurements on the territory of Kyrgyzstan in 2024. KGS24a, KGS24b.
.jpg)